The Gary Division Story: Told by STATS Indiana
This is the 12th article in a series about Indiana's metropolitan statistical areas (metros). All of the data used in this article can be found using the USA Counties and Metros Side-by-Side feature on STATS Indiana (www.stats.indiana.edu).
The Area
The Chicago-Naperville-Joliet metro includes four northwest Indiana counties (Jasper, Lake, Newton and Porter). These four counties, also known as the Gary division, contained about 702,460 people in 2008, making up 7.3 percent of the Chicago metro and 11 percent of Indiana. Between 1980 and 1990, the Gary division saw a decrease of about 40,000 people. By 2000, the population had nearly rebounded and has since surpassed its 1980 level.
The most recent population component trends show that the biggest factor in the Gary division's increased population are from natural increase (more births than deaths). To a much smaller extent, domestic and international migration brought additional residents to the area. The percent of people in each age group was fairly consistent across the Gary division, the Chicago metro, Indiana and the United States (see Figure 1). There was only a slightly higher percentage of older adults in the Gary division and a slightly lower percentage of people in the young adults category.
Figure 1: Percent of People by Age Group in the Gary Division, Chicago Metro, Indiana and the United States, 2007
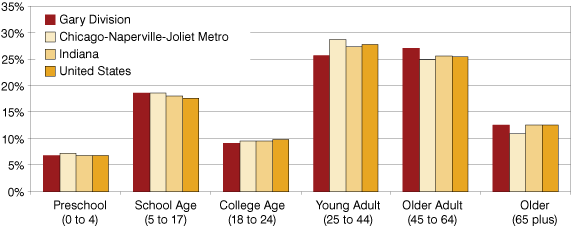
Source: IBRC, using U.S. Census Bureau data
Jobs
Overall jobs in the Gary division followed the same trend as the three other geographies in this article from 1997 to 2007, except that the Gary division started seeing a decline in jobs in 1999 while the Chicago metro, Indiana and the United States didn't start losing jobs until 2000. However, the division also started rebounding a year sooner (2002) than the other areas in this comparison and has been increasing ever since (see Figure 2).
Figure 2: Total Jobs in the Gary Division, Chicago Metro, Indiana and the United States, 1997 to 2007
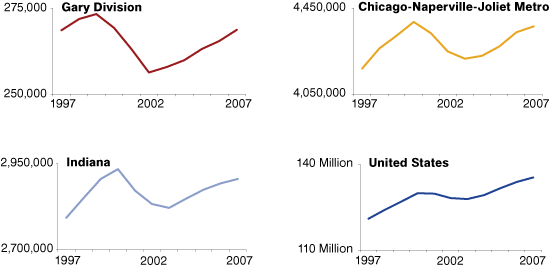
Source: IBRC, using Bureau of Labor Statistics data
While manufacturing had the highest percentage of workers in the Gary division in 2007 (14.2 percent of total covered employment), it was still a lower proportion than that of the state's 18.9 percent of jobs in manufacturing (see Figure 3). Jobs in the health care and social services industry were more popular in the Gary division (13.6 percent of total jobs) than in the Chicago metro as a whole (11.2 percent), Indiana (12.4 percent) or the United States (12.5 percent).
Figure 3: Jobs as a Percent of Total in the Gary Division, Chicago Metro, Indiana and the United States, 2007
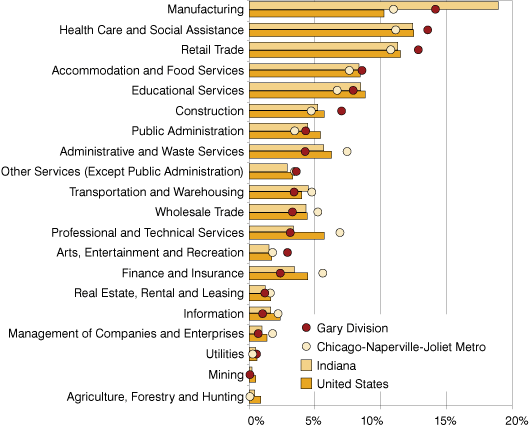
Source: IBRC, using Bureau of Labor Statistics data
Wages
Average annual wages in the Gary division have fallen as a percent of U.S. wages from 1997 to 2007. After adjusting all dollar amounts to 2007 dollars, the Gary division saw an increase of 1.5 percent. Meanwhile, the Chicago metro increased 11.1 percent, Indiana increased 5 percent and U.S. wages increased 11.5 percent.
The highest paying industry in the Gary division, the Chicago metro, Indiana and the United States is management of companies and enterprises. The Chicago metro paid the highest average for this service industry at $116,543. Indiana had the lowest average for management of companies and enterprises, paying an average annual wage of $72,683 (see Figure 4).
Not surprisingly, accommodation and food services was the lowest paying industry across the board. The Gary division paid less than Indiana, averaging $11,427 and $12,452 per year, respectively. The Chicago metro paid the highest in the accommodation and food services industry with an average annual wage of $17,624.
Figure 4: Industry Wages in the Gary Division, Chicago Metro, Indiana and the United States, 2007
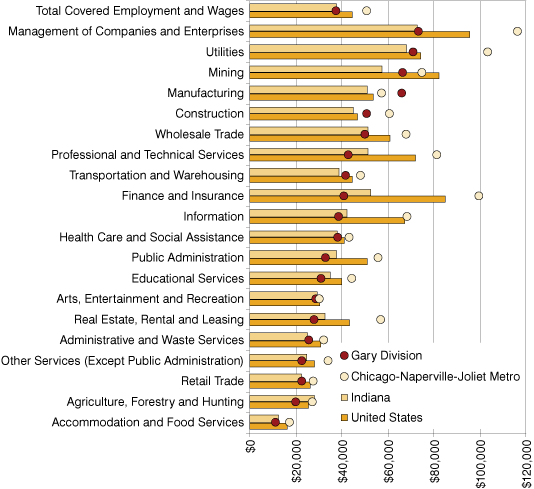
Source: IBRC, using Bureau of Labor Statistics data
Conclusion
As such a small percentage of the Chicago metro, it is not surprising that the Gary division doesn't reflect the metro's demographic and economic trends to the same degree. Both areas grew in population from 1990 to 2008, but the Gary division grew at a much slower pace than the metro. The same was true with jobs from 1997 to 2007 (the Gary division increased 0.1 percent while the Chicago metro increased jobs 4.7 percent). Wages had an even more dramatic difference (a 1.5 percent increase in the Gary division and an 11.1 percent increase in the Chicago metro). Despite the fact that the Gary division is growing more slowly than the metro, there is good news behind these numbers—the Gary division is growing.
Molly Manns, Associate Editor
Indiana Business Research Center, Kelley School of Business, Indiana University
