Property Tax Rates Across the State
This month homeowners statewide paid the first installment of their biannual property tax bill. Property tax liability depends on a number of factors, including where your house or business is located, its assessed value and the applicable deductions, exemptions and credits.
The following discussion uses the 2004 property taxes that were payable in 2005, according to the Department of Local Government Finance. Note that Brown County data are unavailable, so they are excluded from this analysis.
Rates across the State
There are more than 1,950 taxing districts in Indiana, and each sets its own tax rate based on the value of property in its jurisdiction and its estimated budget. (1) The number of taxing districts ranges from 61 in Marion County to five in Ohio County, with a median of 20 taxing districts per county.
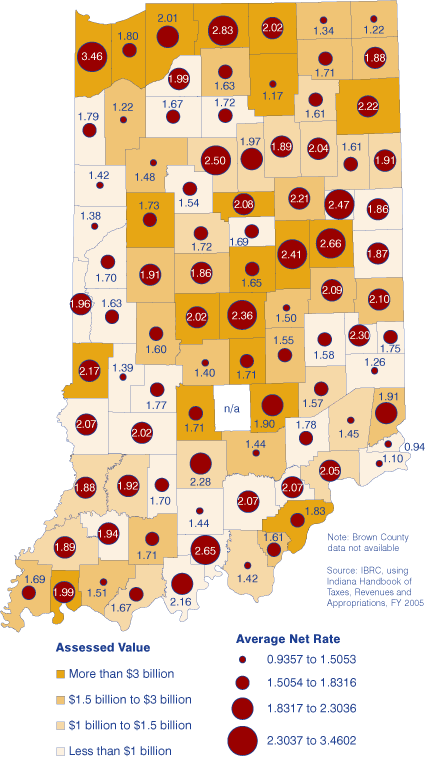
Eighteen of the 20 highest property tax rates are in Lake and St. Joseph counties, led by the Gary-Calumet Township–Gary Schools district at 8.3101 percent. At the other end of the spectrum, 15 of the 20 lowest property tax rates are found in Steuben and Kosciusko counties, with rates below 1.5 percent. Statewide, the median rate was 2.3295 percent, with a slightly higher average rate of 2.4843 percent.
Bear in mind that these statutory rates are not the effective rates most people or businesses pay. A variety of deductions lower one's gross assessed value (GAV), while credits lower the amount of tax owed. The state government lowers the tax bill on all properties through the state property tax replacement credit (PTRC), which is financed by the sales tax, individual income tax and riverboat wagering taxes.
Taken together, these factors can lower the effective rate of taxation quite significantly. Figure 1 shows the net rates (which take into account the state PTRC only) averaged across districts in each county, alongside GAV.
Figure 1: Average Net Property Tax Rate and Gross Assessed Value, 2004 payable 2005
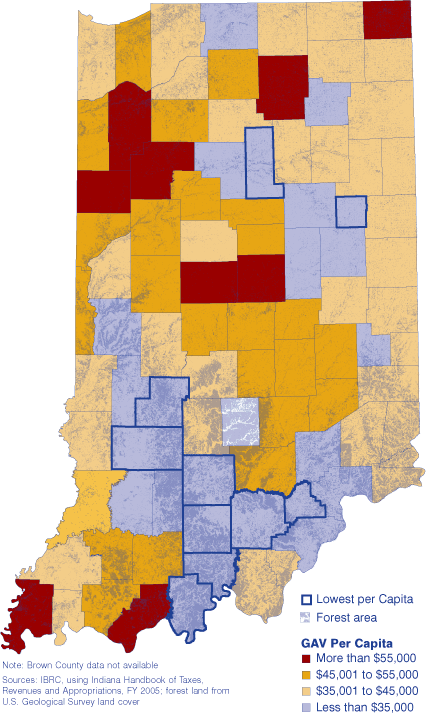
Assessed Value
The total gross assessed value of property for the 91 counties where data are available exceeds $269 billion. As one would imagine, assessed value decreases where rurality increases, as seen in Figure 1. Thus, Marion County's GAV reaches $39.5 billion, whereas Crawford County's GAV is just under $239.8 million. In fact, Indiana's 45 metro counties account for 79 percent of the state's assessed value.
Nevertheless, metro areas do not lead the pack once the assessed value is divvied up among the population using assessed value per capita (see Figure 2). With the 2004 population estimates as the base, per capita GAV averaged $43,288 for the 91 counties. Thirty-six counties exceed the average, led by Steuben County (population: 33,722) with per capita GAV of $77,546. Hamilton County, the fifth most populous county in the state, ranks second with per capita GAV of $70,492.
Figure 2: Gross Assessed Value per Capita, 2004 payable 2005
Eight of the bottom 10 counties are in southern Indiana. With the state's smallest GAV, Crawford County again ranks last with a value of $21,473 per capita. Of course, look at Figure 2 again and note how much of Crawford County is woodland. In fact, most of Crawford and Perry counties are part of the Hoosier National Forest. While not all woodland area shown in the map is classified forest, under state law, land meeting the classified forest criteria is assessed at $1 per acre (although, in the case of the national forests, one should remember that government-owned lands and property are ultimately exempt from taxation). (2) So, considering that southern Indiana has significantly more forested land than northern Indiana, it is somewhat natural that its GAV be lower than it is farther north.
For additional information on how property taxes are calculated or to see a sample bill with definitions of commonly used terms, visit www.incontext.indiana.edu/2006/may/property_taxes.html.
Notes
- For an explanation of how tax rates are determined, see Carol O. Rogers, “The New Age in Indiana Property Tax Assessment” Indiana Business Review (Spring 2005): 2-4; available at: www.ibrc.indiana.edu/ibr/2005/spring/article2.html.
- This law is available at www.in.gov/legislative/ic/code/title6/ar1.1/ch6.html.
Rachel Justis, Managing Editor
Indiana Business Research Center,
Kelley School of Business, Indiana University